With two ‘once in a century’ events in less than two decades adding more than £1tn to public debt, it is unsurprising that the OBR’s Fiscal Risks Report published earlier this week places much more emphasis than previous reports on the potential for catastrophic risks, whether that be from further pandemics, major wars, climate change or cyberattacks.
The report focuses on three particular risks: the coronavirus pandemic, the cost of debt, and climate change, with the latter being the subject of the #icaewchartoftheweek.
The OBR distinguishes fiscal risks from climate change between those stemming from global warming itself (physical risks) and those relating to the move to a low-carbon economy, including the policies to achieve that (transition risks). In unmitigated climate change scenarios, the physical risks dominate, whereas the more that is done to mitigate global warming by reducing emissions, the more important transition risks become.
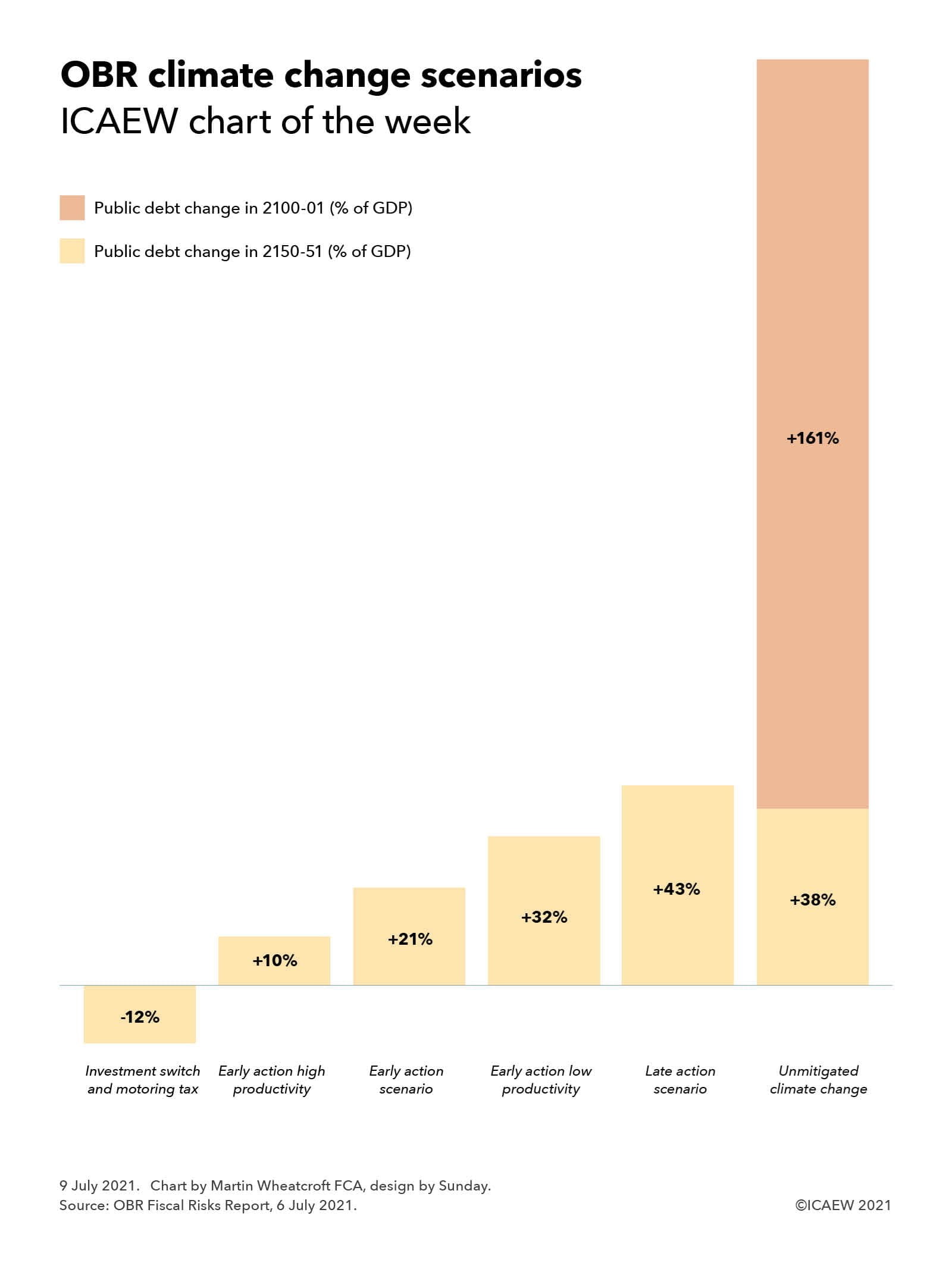
The chart illustrates two main scenarios explored by the OBR – an early action scenario where the UK and other governments around the world push forward with plans to achieve net zero by 2050 and a late action scenario where the UK government delays taking actions to decarbonise the economy. The chart also shows three variants on the early action scenario depending on whether decarbonisation boosts or damages productivity or where investment is switched from other areas and motoring taxes retained.
In the early action scenario, the OBR estimate that public sector debt would rise by 21% of GDP by 2050-51 (equivalent to £469bn in current prices) as a consequence of lost fuel duties and other taxes of 19%, additional spending of 6%, indirect economic effects of 6% and interest on borrowing of 4% less 14% from carbon taxes imposed to incentivise the shift to net zero.
The high productivity variant is similar in terms of costs and carbon tax receipts, but with indirect economic effects contributing additional tax receipts with a consequent reduction in borrowing costs over 30 years, resulting in net additional debt of 10% of GDP. The low productivity variant assumes the reverse with lower tax receipts and a smaller economy combining to increase the net increase in public debt to 32% of GDP. The other variant identified by the OBR has the effect of reducing public debt, where investment in decarbonisation is funded by cutting other public investment plans and existing motoring taxes are shifted onto electric cars to retain that source of income to the exchequer.
A key finding in the report is that delaying action would cost a lot more than moving early with public sector debt rising by 43% in 2050-51, more than double the early action scenario, as it would require a more radical intervention costing more and resulting in more adverse economic effects.
Ironically, the OBR estimates that doing nothing would have a smaller impact on net debt by 2050-51 than the late action scenario as decarbonisation costs would not be incurred. However, the OBR estimates that unmitigated climate change would have a significant impact for the rest of the century, with public debt potentially rising to 289% of GDP by 2100-01 if action is not taken to prevent temperatures rising around the world.
For more information read the OBR Fiscal Risks Report.
Join the Public Sector Community
For accountants and finance professionals working in and advising the public sector, this Community is the go-to for the key resources and guidance on the issues affecting practitioners like you. With a range of dynamic services, we provide valuable tools, resources and support tailored specifically to your sector.

