The Home Office published its Annual Report and Accounts for the year ended 31 March 2023 on 19 September 2023.
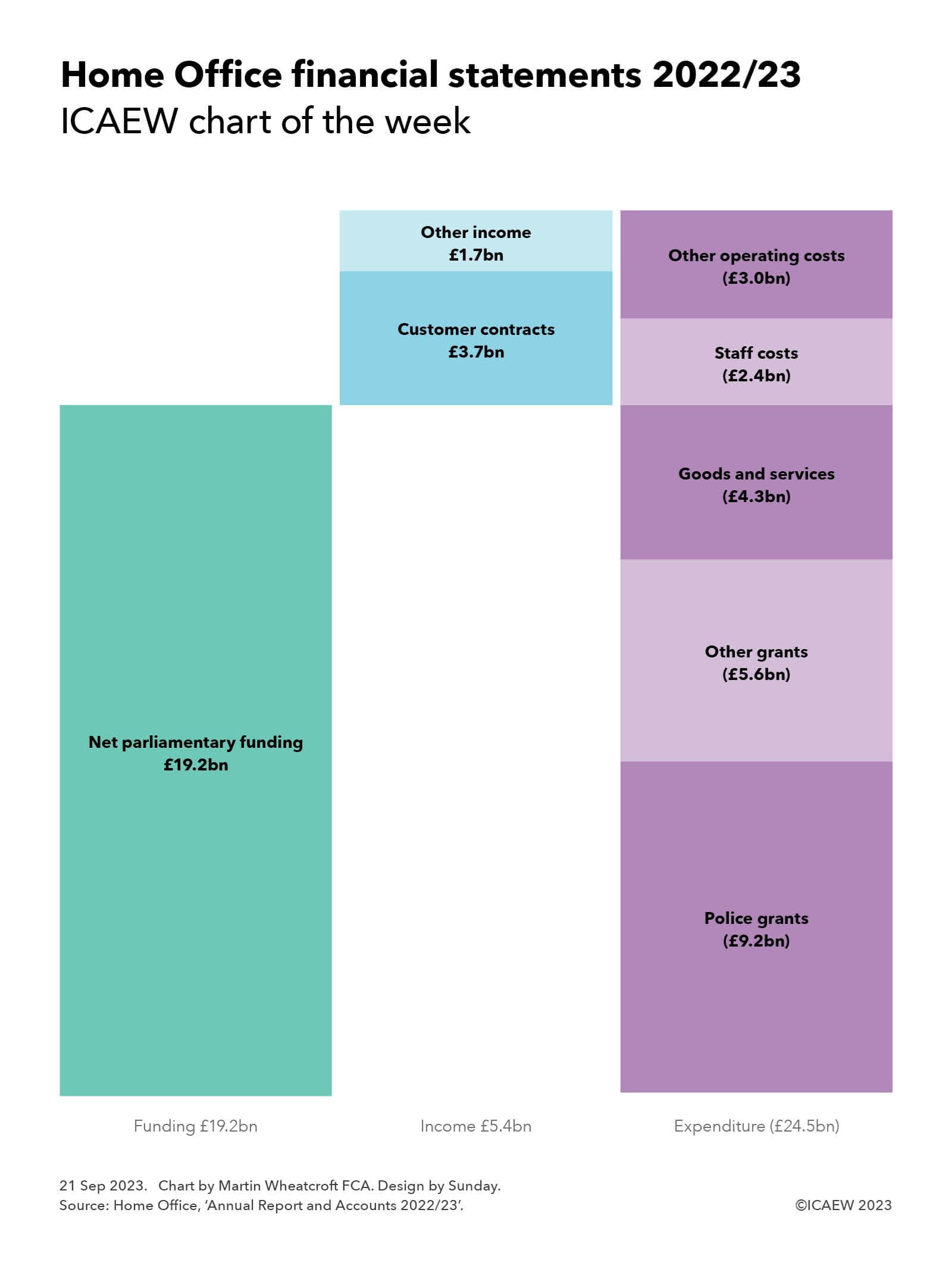
Net expenditure in 2022/23 was £19.1bn, comprising expenditure of just over £24.5bn net of income of £5.4bn, while parliamentary funding net of other items amounted to £19.2bn.
The Home Office breaks down its income for the year of £5.4bn between revenue from contracts with customers of £3.7bn and other income of £1.7bn. The former includes £2.2bn from visa and immigration charges, £0.6bn in passport fees, £217m for the disclosure and barring service (DBS), and £0.7bn from other sources. Other income is primarily comprised of immigration health surcharges payable by foreign residents and visitors for the use of the National Health Service, a proportion of which is transferred to the Department of Health and Social Care and the devolved administrations.
As our chart this week illustrates, the majority of the Home Office’s spending is in the form of grants. The largest grants, totalling £9.2bn, are to local police forces across England to supplement the council tax precepts they raise locally. Other grants include £1.7bn to top up police pensions, £0.4bn to top up fire and rescue services pensions, £3.3bn in other operating grants (many of which also go to police forces, in addition to transfers to other government departments) and £209m in capital grants.
Purchases of goods and services of £4.3bn is dominated by the £3.1bn paid in relation to asylum and detention, together with £287m in facilities management and staff services, £229m on professional fees, £219m for media and IT, £169m for passport printing and stationery and £120m for visa and immigration commercial partners amongst other costs.
Staff costs of £2.4bn cover the costs of employing full-time equivalent averages of 41,607 permanent staff, seven ministers, seven special advisers, and 6,489 other staff during 2022/23. Wages and salaries amounted to £1.8bn, equivalent to an average full-time equivalent salary of £37,900.
At 31 March 2023 there were 345 senior civil servants on salaries in excess of £70,000, of which 251 were between £70,000 and £100,000, 86 between £100,000-£150,000 and eight between £150,000 and £190,000. The average of seven government ministers who served during the year (a total of 22 different individuals!) earned the equivalent of an average annual salary not including pension entitlements of around £49,000 in addition to their parliamentary salary or House of Lords attendance allowances.
Other operating costs of £3.0bn include £1.6bn on IT and accommodation-related service charges, £0.7bn for depreciation and amortisation of assets, and £113m in asset recovery costs together with other costs.
Parliamentary funding net of other items of £19.2bn is reported in the consolidated statement of taxpayers’ equity and comprised £19.4bn in drawn-down parliamentary funding, £0.3bn in deemed funding less £0.5bn in amounts repayable.
Not shown in the chart is the Home Office’s consolidated balance sheet, which comprised £2.6bn in non-current assets, trade and other receivables of £0.7bn and cash and cash equivalents of £0.6bn less trade and other payables of £3.7bn, £0.6bn in lease liabilities and £0.5bn in provisions to give net liabilities of £0.9bn.
Reported in the notes to the accounts are £0.8bn in capital additions, of which £374m was incurred on software and other intangible assets.
Find out more: Home Office annual report and accounts: 2022 to 2023