The recent publication of the Department for Business, Energy & Industrial Strategy (BEIS) accounts for 2020-21 contained an assessment of the losses expected on the financial provided to businesses through the Bounce Back Loan Scheme (BBLS), the Coronavirus Business Interruption Loan Scheme (CBILS), the Coronavirus Large Business Interruption Loan Scheme (CLBILS) and the Future Fund. This was followed by an updated report from the National Audit Office (NAO) on the administration of the scheme and the potential losses to the taxpayers.
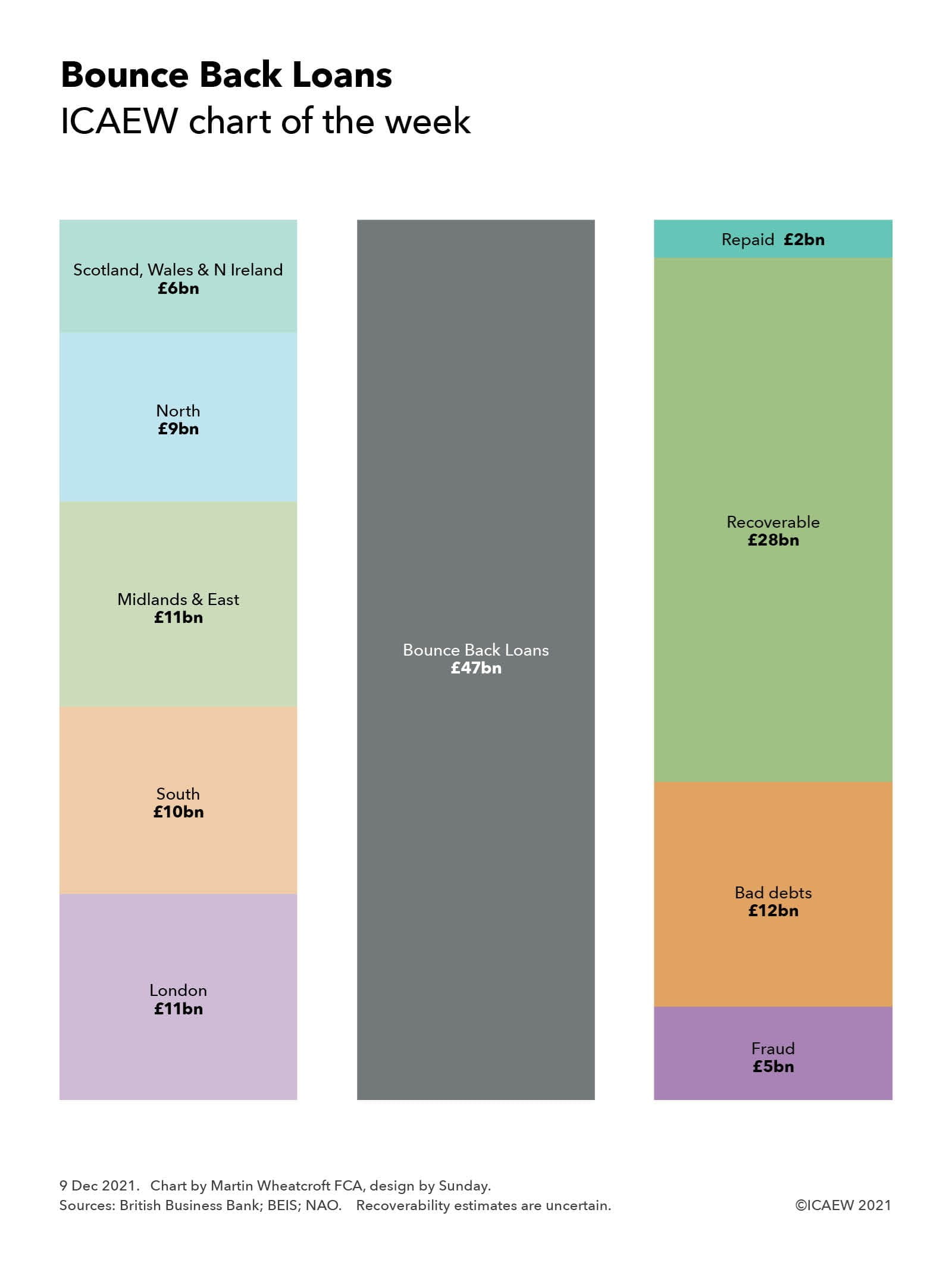
The largest of these schemes was BBLS, with Bounce Back Loans of up to £50,000 provided to eligible businesses to help them weather the first lockdown in the second quarter of 2020, before being extended to the whole of the 2020-21 financial year. In the end, around a quarter of businesses took out a Bounce Back Loan, comprising 1.5m loans for a total of £47bn at an interest rate of 2.5% repayable over six years. The interest in the first year was covered by the government, with no repayments due in that period.
Businesses can extend the loans to ten years through the Pay As Your Grow option, as well as being allowed up to one six month payment holiday and three interest-only payments to provide flexibility without going into default.
The seven main UK banks provided around 90% of the loans by value, with the rest provided by other banks and non-bank lenders, such as peer-to-peer lenders. Each participating financial institution was provided with a 100% guarantee by the government to cover any amounts not repaid. Half a million or nearly 35% of the loans were for the maximum amount of £50,000 (adding up to £27bn) with £18bn lent out between £10,000 and £50,000 and £2bn lent for amounts between £2,000 (the minimum possible) and £10,000.
As the chart illustrates, the geographical distribution of loans was weighted towards the south and centre of England, with £11bn borrowed by businesses in London, £10bn in the South (£6.5bn South East and £3.6bn South West) and £11bn in the Midlands & East (£3.8bn West Midlands, £2.9bn East Midlands and £4.5bn East of England), a total of £32bn. The balance of £15bn was split between £9bn in the North (£3.2bn Yorkshire & the Humber, £4.8bn North West and £1.3bn North East) and £6bn in the other nations of the UK (£2.7bn Scotland, £1.6bn Wales and £1.3bn Northern Ireland).
More than 90% of the loans, amounting to £40bn, went to micro-businesses, ie businesses with turnover below £632,000.
BEIS have estimated in their 2020-21 financial statements that they do not expect 37% of the loans with a value of £17bn to be repaid, comprising £12bn in estimated bad debts and £5bn in estimated losses from fraud, although the NAO says that these numbers are highly uncertain at this stage. With £2bn already repaid, this leaves £28bn believed to be recoverable over the remainder of the six years of the loans (or 10 years for those that are extended).
The fraud estimate, for 11% of the loans with a value of £4.9bn, was based on a sample of 1,067 loans as at 31 March 2021, but a subsequent analysis in October 2021 suggests that the level of fraud may be lower at around 7.5% of loans and so there is some hope that BEIS and the British Business Bank will be able to reduce the amount they will have to reimburse to participating banks under the 100% guarantees.
However, as the NAO reports, these guarantees mean participating banks have no financial incentive to chase repayment and it has raised concerns that insufficient resources are being dedicated by BEIS and the British Business Bank to recovering outstanding amounts.
The challenge for government is that many businesses have not been able to get back to their pre-pandemic level of operation and so there is a need to be sensitive, whilst at the same time seeking to protect public money and tackle those who made fraudulent claims.


