Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) are reserve assets issued by the International Monetary Fund (IMF), the ‘international central bank’ for central banks.
Just as national central banks create money by issuing currency in exchange for debt, the IMF creates its own form of ‘international money’ in the form of SDRs, balanced by long-term debt owed to the IMF by its member countries.
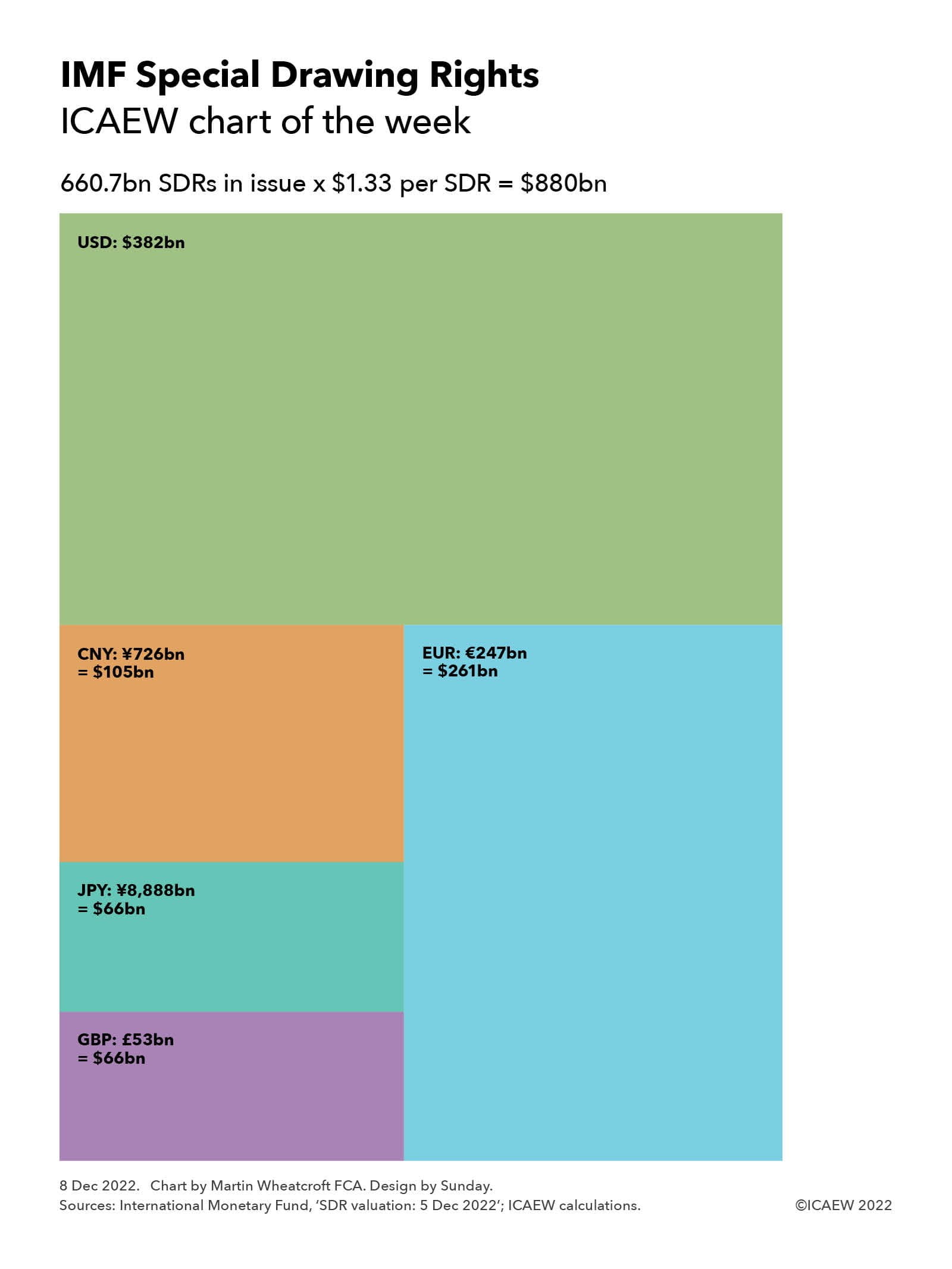
To date, the IMF has issued 660.7bn SDRs, most recently in August 2021 when 456.5bn SDRs were issued to provide additional liquidity to member countries during the pandemic.
Countries are able to exchange the SDRs they are issued with for the underlying currencies that make up each SDR, providing them with international liquidity when they need dollars, euros, yuan renminbi, yen or pounds sterling or – in many cases – just dollars. According to the latest five-year currency weightings determined in July 2022, 1 SDR should be exchangeable for 0.57813 US dollars, 0.37379 euros, 1.0993 Chinese yuan, 13.452 Japanese yen and 0.08087 UK pounds.
Our chart illustrates what this means for the total of 660.7bn of SDRs in issue, which as of 5 Dec 2022 was calculated to be worth approximately $880bn in total based on a value of $1.33 per SDR. The total comprised $382bn in US dollars, €247bn in euros (worth $261bn at 5 Dec 2022), ¥726bn Chinese yuan ($105bn), ¥8,888bn Japanese yen ($66bn) and £53bn in UK pounds ($66bn).
In effect, 43.4% of the currency basket making up each SDR was US dollars, 29.7% was euros, 11.9% was Chinese yuan, 7.5% was Japanese yen and 7.5% was UK pounds.
Despite SDRs being an ‘international reserve asset’ that central banks and member countries can use to manage their own currencies, the IMF insists that SDRs are not a currency in their own right. Instead, it stresses that SDRs are merely an ‘accounting unit’ to be used for IMF transactions. However, despite these protestations, the IMF has concluded that SDRs are the functional currency for the purposes of its financial statements prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards.
The strength of the dollar means that SDRs at $1.33 each are worth $56bn less than the blended average rate of $1.42 each when they originally issued. This is because the non-dollar components of the currency basket, especially the euro and sterling, have fallen in value in relation to the US dollar in recent years.
At less than a trillion dollars, SDRs may seem quite small in comparison with the vast flows of money around the world. However, their importance to the international monetary system cannot be understated, keeping the financial wheels turning and providing central banks (especially those in smaller nations) with essential liquidity when they need it most.